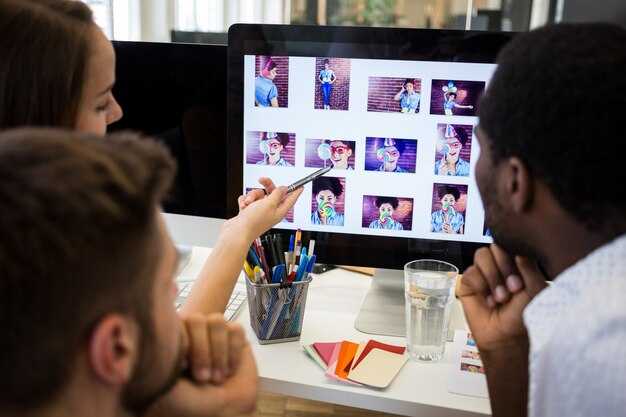
Прийміть рішення. hybrid workflow: let AI-assisted tools shoulder repetitive data tasks while the crew preserves control over look and storytelling. This approach gives more latitude to iterate quickly while maintaining artistic intent, and it sets expectations for on-set and post-production collaboration.
In practice, teams leveraging this model report ефективність gains on loose ends and a large decrease in turnaround time across locations and shoots. generated previews accelerate the chasing of the right look and help with adjustments before final capture. The pipeline becomes virtual and hybrid by design, enabling more options for packaging assets and distributing to partners. often, this approach supports several parallel workflows and scales across several large shoots.
However, there are pitfalls to manage. Without disciplined oversight, alignment to brand and temperament can drift, as look becomes a crusade for gloss rather than truth. The complex scenes with multiple locations and lighting require careful adjustments and a human check in post-production. The approach should not chase novelty at the expense of reliability; otherwise, the works of the crew suffer and output quality can degrade over time.
To maximize value, choose tools that track progress across locations and stages, and that offer clear control surfaces for adjustments. Start with several pilot tasks and measure impact on ефективність and on the pace of packaging of assets. Keep the crew involved in setting limits for output quality, while AI handles repetitive edits, color matching, and thumbnail generation for quick reviews. This gives you a scalable path toward a virtual pipeline while preserving the human sensibility that audiences expect.
In short, AI-enabled tools help the crew improve output without erasing the creative core. They can handle complex tasks, free the crew to focus on storytelling, and increase the pace of post-production. The decision hinges on a deliberate plan: define responsibilities, measure impact, and supporting helping collaboration between human and machine.
Practical viability, costs, and workflows for AI video generation
Start with a two-week pilot using a single model family to produce short image-to-video reels and measure time-to-delivery against a manual baseline. This yields true data on throughput and reveals where automation adds value without eroding craft.
- Viability levers: constrain scope to short formats, rely on a centralized system that handles asset ingestion, rendering, and delivery; ensure algorithms cover lip-sync, exposure, and color grading at a baseline quality; use assets from studios’ decks; include a human-in-the-loop editor for emotional beats.
- Costs and budgeting: track costs across licensing, compute, storage, data transfer, and editor passes; aim for a cost-per-minute well below traditional production for routine clips; explore usage-only licenses and tiered compute to stay within budget; plan for a marz dataset expansion if needed.
- Quality controls: implement automated checks for alignment with scripts, realism of movement, and consistency across scenes; require a final pass by an editor for delivery-ready outputs; set ideal targets for high-quality 1080p or 4K where required.
- Risk management: define guardrails on content safety and brand exposure; maintain versioning and audit logs; ensure scripts are stored in a deck for quick reference.
- Brief and scripts: collect script notes, key emotional beats, and shot list; map to assets for image-to-video generation.
- Asset ingestion: pull licensed images, product shots, and stock elements; organize in a system with exposure and color profiles.
- Draft generation: run automated passes to produce multiple variants; use different prompts or seeds to diversify outputs and mimic different aesthetics.
- Post-processing: run lip-sync checks, adjust exposure and color, apply motion stabilization if needed; hand off to editor for final polish.
- QA and iteration: compare to scripts, measure timing, check brand alignment; iterate quickly with tight cycles.
- Finalization: export reels in required formats for decks and social; generate alternate versions for different platforms; document learnings in a corporate deck.
What production tasks can AI cover today?
Implement AI for three immediate tasks: transcript generation from draft scripts, rapid iteration of shot lists, and visual concept framing. Use avatar to sketch scenes and follow camera cues; leverage davinci for first drafts and set boundaries to keep outputs aligned. These steps reduce manual edits and shorten turnarounds; studies show 30-50% time savings on initial drafts and planning. Different creators can tailor prompts to everyday workflows; this offering is accessible across multiple studios. Resulting transcripts, visuals, and shot outlines become visible early to stakeholders, enabling faster feedback loops. Additionally, generating refined visuals from prompts accelerates iteration and better alignment with marketing goals.
Additionally, recognition features support generating transcripts and captions, improving searchability and reuse. These capabilities tag dialogue and scene elements, speeding asset discovery and reuse across campaigns. Marketing-focused outputs include ready-to-publish hooks, thumbnails, and short clips generated from the same prompts, also reducing fragmentation across campaigns. This approach ties AI outputs to an offering-friendly workflow that supports follow-up iterations toward better results.
Iterative flows: after the initial pass, a creator reviews visuals, shots, and transcripts; update prompts for the next iteration; this loop speeds accuracy and keeps the output aligned with visible requirements. Use cloud-based services to generate assets for different formats and reuse visuals across campaigns. Additionally, maintain a two-pass workflow: generation followed by human validation before finalizing visuals.
Boundaries for ethical use: store prompts and outputs with provenance; respect licensing for assets and likeness. World-building with avatars and variable shots remains dependent on human direction; AI handles routine parts, but the creative spark stays with the creator. The offering grows with services supporting different formats: long-form, short-form, and interactive experiences. Also, track data handling, consent, and licensing to protect everyday workflows and marketing programs; this keeps the process transparent for stakeholders.
What AI still misses in scripting, storyboarding, and supervision?
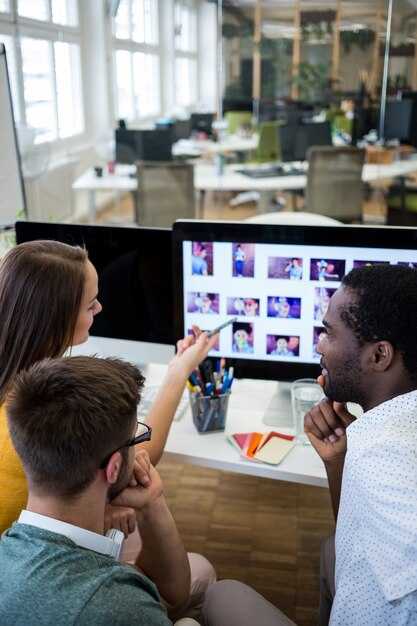

Keep a human-in-the-loop in pre-production; AI can draft outlines and scene blocks, but final scripting and storyboard decisions stay with trained writers and artists in an end-to-end workflow.
Scripting gaps: AI tends to misread meaning and emotional intent, producing lines that sound plausible but land flat for most audiences. It relies on temp data and popular presets, and while it can imitate tone, it lacks cultural nuance across businesses and corporate contexts. It can remove subtle hints and turn moments of subtext into obvious beats, creating emotional noise. For best results, run AI drafts through a trained editor who can preserve intent, adjust pacing, and keep users engaged. Use presets to align tone, keep data checks, and verify facts before any decisions using pre-production prompts.
Storyboarding gaps: AI can propose frame grids, but misses physical constraints, blocking, and shot-language that works on actual sets. It misreads looking direction, misweights scale, and can’t reliably model lighting, reflections, or actor movement without a defined environment. This reduces turns in the revision cycle and helps ensure faster alignment. Use AI to generate several framing options, then have a trained supervisor define blocking and camera directions, turning each panel into a concrete shot list. This end-to-end workflow helps preserve meaning and reduces back-and-forth on-set decisions.
Supervision: AI lacks accountability, can’t gauge team reaction on set, and cannot substitute real-world ethics checks. It can’t replace experienced oversight, especially for safety, compliance, and on-set coordination. Rely on trained editors to monitor outputs, annotate risk points, and adjust prompts; maintain a clear log that records decisions, turns in the feedback cycle, and rationale. This keeps corporate standards and reduces misalignment, while enabling affordable controls for businesses of every size.
Best practices: keep data clean and organized; separate source material from AI outputs; maintain a reusable library of prompts and presets; ensure consent for cloning or style-matching; avoid leaking sensitive data; create a process to save and audit decisions; plan for wind-down if outputs drift from brand voice. Define the mean message of each scene to avoid drift and keep the tone consistent. Use an end-to-end pipeline that integrates AI drafts with human reviews, and store logs to reveal how decisions were made, which helps auditability and learning for users. This approach also helps maintain meaning across revisions and reduces emotional misreads.
Practical steps: define a pre-production style guide, build a shared library of prompts, and implement an end-to-end workflow where AI drafts save time and are refined by trained professionals. When integrated with discipline, AI becomes a time-saving tool rather than a source of drift. Start with small experiments to find what turns out better for most users, and keep a clear log to show what data and meaning guided each choice. Use cloning only with explicit consent, and routinely assess outputs for bias. This approach keeps businesses affordable and ensures outputs reflect brand voice across every asset.
Descript – AI Audio + Video Transcript Editor: core features in real projects
Use Descript as the primary hub for fast, ai-powered transcription and editing in real projects; built to fuse transcript, audio, and visuals inside a single system, it shortens review cycles and reduces back-and-forth with partners.
Core features in practice include automatic transcription with speaker labeling, punctuation, and search; a timeline that lets you edit text to trim the audio, then re-export as a finished asset; overdub and text-to-speech options for quick voiceovers; an image and photos asset library that syncs with transcripts inside the workflow.
Within shoots, you can experiment with multiple packaging variants for clips and social cuts; the tool exposes presenters and performances, allows quick swap of shots, and keeps emotion and natural performances aligned with the script.
Access is open across teams; spending on tooling decreases when you reuse assets inside the project; the soulid focus on artistry helps maintain emotion even under pressure as you study the material and shoot optimally.
| Feature | Impact in real projects | Нотатки |
|---|---|---|
| Transcript-driven editing | Speeds cuts; text-to-timeline linking enables quick refinements of shots range | Inside the editor, changes propagate to audio and visuals |
| ai-powered transcription with speaker labeling | Reduces manual notes; improves coherence across presenters | Supports open captions for accessibility |
| Overdub and voiceover tools | Expedites voice additions; lowers the need for re-shoots | Useful when shaping emotion and tone |
| Asset library integration (image, photos) | Faster packaging of clips; aligns visuals with transcript cues | Asset inside; supports quick experiments |
| Collaboration and access controls | Improved coordination across contributors; reduces pressure on single editors | Permissions keep projects organized |
| Export formats and packaging | Ready-to-publish assets in a range of formats | Supports client-ready deliverables without rework |
| Audio-video timeline synchronization | Smooth alignment of performances with script; natural pacing | Essential for live-shoot planning and post |
Hybrid workflows: integrating AI with human editors and directors
Adopt a two-track pipeline: automate rough cuts, scene tagging, and metadata with AI, while editors and directors refine storytelling, pacing, and performance to ensure authenticity, continuity in post-production.
Implementation steps: ingest footage and audio; AI scans background content, identifies shots, and composes quick, alternate sequences. The builder surfaces options, including dubbed audio tracks, quick swaps of music, or background tones. Human craftspersons review, select among options, and lock decisions for each part.
Tech specifics: Use a machine-learning module in software such as davinci and premiere to auto-tag what’s in each shot, surface quick clips for review, and generate alternate sequences, which can be automatically adjusted to fit feedback. In the background, chatgpt can draft notes for the director, and the builder can assemble candidate cuts that mimic the tone of the session. Editors and directors then validate, flag continuity issues, and record decisions for archive.
Their collaboration should prioritize authenticity and flexibility: directors provide the emotional arc and timing, ensuring automations do not erode the audience’s immersion. Editors tailor AI-suggested sequences to performers’ delivery, pacing, and style, ensuring the result feels human rather than mechanical. Dubbed audio or subtitling can be layered later if needed without sacrificing voice. Instead, we emphasize human oversight to preserve the human touch and connection.
Outcomes and governance: Define clear milestones in streaming-ready workflows, where AI analytics feed decision points for color, pacing, and transitions, and leverage features like versioning, notes, and audit trails. Automate repetitive tasks, but retain human oversight to maintain a coherent voice and to pivot quickly on feedback. This approach supports rapid iteration across formats, from short-form to long-form, while keeping a unified backbone across what matters.
Costs, licensing, and data privacy risks for AI video tools
Implement a licensing framework and a data-handling clause before any upload. Secure ownership of outputs, restrict data used to train models, and require an option to disable training on client assets. Favor vendors offering on-prem or isolated cloud options to guard assets, and align controls with studio workflows and the lip-sync capabilities of the toolkit.
Costs and licensing models to compare: per-seat subscriptions, tiered access, and usage charges for image-to-video generations; storage and API fees add to the bill; equipment needs are reduced, yet the work remains in human oversight, keeping total ownership manageable. Map the cycle across legacy workflows, handoffs between roles, and the potential rework when generations do not satisfy the brief; quantify cost by minutes generated and assets stored.
Data privacy considerations: ensure encryption in transit and at rest, and define who owns inputs and outputs. Determine if inputs may be used to train models and set retention windows or deletion rules; require regional data handling and clear jurisdiction. Demand a data processing addendum (DPA), audit rights, and strict access controls by roles; specify that image-to-video tasks involving confidential assets stay within defined boundaries. They remain under contract.
Governance and handoffs: create a compact toolkit for creators and editors that defines when to generate, how to review, and who holds judgment on final outputs. Define roles and enforce handoffs between producers, editors, and IT. Keep a log of versions and context for each pass, preserve equipment discipline, and ensure the studio retains final say on sensitive edits. This approach reduces misalignment and keeps ownership aligned with the brand direction.
Practical checks and numbers: aim for a mid-size studio with five seats; base licenses range US$20–US$150 per seat per month; per-minute generation charges commonly US$0.10–US$3 depending on resolution and model; storage around US$0.01–US$0.25 per GB per month. Add internal labor for reviewing outputs and managing handoffs; track total spend monthly and revisit terms annually to catch inflation or shifts that alter the cost structure.

 Can AI Video Generators Replace a Full Production Team? Pros & Risks" >
Can AI Video Generators Replace a Full Production Team? Pros & Risks" >