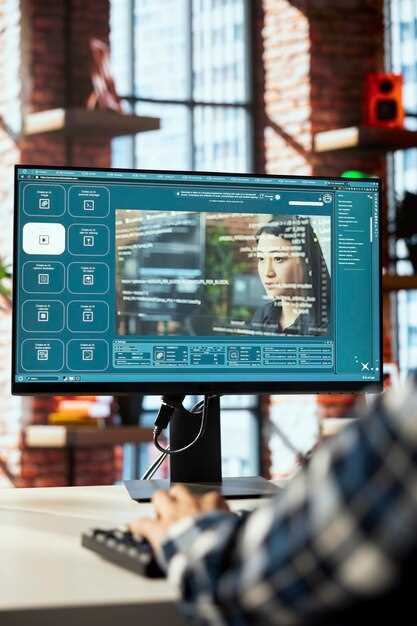
Begin by deploying AI-driven post-production suites that provide automated scene tagging and rough-cut suggestions within days. In recent trials across multiple studios, efficiency gains of 30–50% on first assemblies were observed, while creative control remained intact. This approach provides cloud-native technologies to present scalable workflows and enables crews to utilize high-motion footage more effectively.
Guiding principles center on non-destructive refinements, semantic tagging, and emotional storytelling alignment. Principles support efficient collaboration and knowledge sharing, ensuring metadata guides cut decisions, while previews preserve film tone across variants. This approach can become a standard for every project by reusing a common asset catalog, ensuring true consistency.
Advancements in neural analysis and audio-visual alignment enable accurate tempo, mood, and pacing adjustments without manual frame-by-frame work. Recent advancements allow you to utilize speech-to-text, scene detection, and color-science models to produce a near-professional air in minutes. For practitioners of film and clip production, this means you can begin to explore multi-variant cuts that remain similar in vibe while tailoring for different audiences.
Present implications for producers, editors, and brands include faster time-to-market, lower costs, and more predictable outcomes. know that automation is not a replacement but a support system that provides creative freedom at scale. It’s crucial to measure user satisfaction and align with principles to avoid generic output that lacks emotional resonance with audiences.
To begin implementing at scale, map a lightweight pipeline: ingest, automatic tagging, rough assembly, human review, and final polish. Technologies should be selected for interoperability and efficient rendering. Ensure you present clear metrics on render time, cost-per-minute, and impact on audience engagement, and continuously know and adjust based on findings.
As practices mature, editor roles become more strategic, focusing on storytelling value while automation handles repetitive tasks. Utilize feedback loops to refine presets, and let reelmindais-inspired settings evolve to become true benchmarks across every production.
Online Video Editing: The Rise of AI Tools and the Evolution to Photorealistic Video Generation
To improve capability and publish assets confidently, craft a workflow built on trained models, robust technology, and disciplined testing. Start with a clear objective, conceptualize the target look, and outline prompts that drive each stage. Discussing reference footage, blocks, and combining traditional effects with AI-generated frames yields an excellent baseline for rendering quality. An initial plan should identify barriers, map common failure modes, and establish a collaboration loop with collaborators to leverage analyses across pages of data.
For selecting prompts, build templates that map to three core styles: neutral, stylized, and photoreal. Use a reference library of scenes, textures, and lighting to calibrate outcomes. Maintain a versioned prompts catalog so you can reproduce novel variants while preserving consistency. Test initial variants against objective metrics like temporal coherence, color accuracy, and keep a log of results for future analyses.
Barriers include compute costs, licensing models, and data privacy. To mitigate, prefer on-prem or hybrid testing with capped usage, implement licensing checks on outputs, and schedule testing cycles to validate outputs before publish. Maintain a common notebook of tests with analyses, and share learnings with team to accelerate progress. Use a modular tech stack that can adapt to new models while keeping risk manageable, relying on robust data governance to keep outputs compliant.
Adopt tooling that supports memory of scenes, reelmind, to recall reference frames and reduce redundant prompting. Use this approach to accelerate iteration, lower render budgets, and improve consistency across shots. As you refine, aim to master a core set of rendering primitives and keep a concise reference page for collaborators.
To stay capable against rivals, combining 3D hints with 2D prompts and render pass fusion, using a stable pipeline that supports batch processing on large datasets. The approach leverages a test suite with objective metrics, including lumen consistency and motion fidelity, and publish results to demonstrate progress. When selecting hardware, prioritize GPUs with ample memory and fast matrix operations to cut iteration times, and design a process that protects intellectual property while enabling collaborative R&D. Let them see the practical gains your team delivers. The approach leverages automated checks to validate outputs.
Across project pages, maintain an excellent set of reference materials and a public-facing demonstration reel. Use analyses from each render to refine prompts, and keep a common standard for tones and lighting so that outputs from different artists remain cohesive. This collaborative approach helps competing groups catch up without compromising intellectual property.
Establish a governance checklist for publish-ready outputs: verify consent, avoid misrepresentations, and document prompts used for each clip. Provide clear attribution and track provenance in pages and logs, which helps when collaborating with partners or passing work to rivals for benchmarking. Use clear metrics to track improvement and ensure alignment with brand guidelines.
Recommended actions: assemble a cross-disciplinary team of technologists, artists, and product leads; define 3 initial projects with varied prompts and reference materials; run weekly testing cycles with concrete metrics; document outcomes on pages for transparency; schedule quarterly reviews to discuss improvements and roadmap.
Applying AI Video Generation: Practical Stages from Pixel-Level Edits to Photorealism
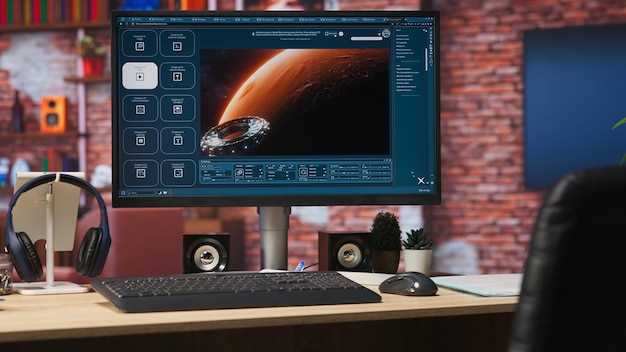
Start with a six-second pilot using a compact dataset and a fixed prompt set to validate the workflow before scaling.
-
Seed creation: perform pixel-level edits on reference frames to establish precise shapes, textures, and lighting cues. Translate edits into a tight prompt bundle for a text-to-video chain. Have a baseline frame that can be reused as a template for other shots, ensuring consistency across the sequence.
-
Prompt engineering and automation: design prompt templates that capture the objective details–lighting, camera angles, material properties, and motion intent. Use gen-4 automated engines to convert prompts into initial frames, then validate with small batches. Open ecosystem by linking assets, references, and configurations in a central repository; this ensures a scalable workflow and easy collaboration. Start building a links library for prompts and assets to accelerate iteration.
-
Coherence and alignment: anchor key elements to control points (pose, lighting direction, color balance) to maintain frame-to-frame consistency. Streamline the process with automated keyframe rules and an interpolation pass that preserves texture and shading, reducing flicker. Which integrates motion constraints and occlusion handling to stabilize the sequence across scenes.
-
Photorealism and texture: refine skin tones, fabrics, reflections, and micro-details with physically based shading and calibrated color transforms. Ensure lighting remains consistent across shots and apply granular color grading and grain to unify the sequence–from shadows to highlights–without washing out details.
-
Motion, camera, and composition: introduce natural camera dynamics, depth of field, and motion blur. Validate with optical-flow-driven stabilization and frame-rate matching. Begin with a few test takes, then expand to longer runs to catch artifacts early and adjust prompts accordingly.
-
Post, optimization, and delivery: perform color grading, denoise, and dithering; compress with a target bitrate to preserve detail. Optimize for distribution across popular platforms, add captions and scene metadata, and prepare versions for different aspect ratios. This optimization supports revenue goals by matching formats to audience preferences and advertising requirements.
-
Evaluation, sharing, and feedback loops: build objective metrics for temporal coherence, perceptual quality, and prompt fidelity. Share results with collaborators through links and screenshots, then refine prompts and assets. This collaborative loop makes sure the workflow improves over time and supports democratizing access to high-quality outputs.
The approach opens an ecosystem that connects artists, technologists, and marketers, which integrates text-to-video prompts with automated pipelines. It empowers teams to publish cinematic pieces that can be repurposed across training reels, commercials, and short films, while maintaining a clear revenue path through licensing, freelance work, or in-house production services. By choosing targeted applications and optimizing prompts for each objective, creators can begin rapidly, share results, and scale production–from initial concept to photoreal finishes–without sacrificing control over artistic direction.
How to choose a browser-based AI editor for scene-aware trimming and color matching
Choose a browser-based editor at forefront of scene-aware trimming and color matching. It should offer a robust library of presets, automation that speeds workflows, and a seamless path to faster, more consistent outputs across shots.
Assess safety features and setups: non-destructive adjustments, safe exports, color-space options, and compatibility with current software.
Scene segmentation accuracy matters for preserving angles and pacing. Prefer tools that automatically detect cuts and let youre able to override with precise trim points when needed.
Color matching across shots is critical for immersive productions. Look for automatic color alignment across frames, LUT support, and a simple interface to tweak curves while preserving natural lighting.
Performance checks: run basic projects on common setups; measure latency and projected time reductions during exploration.
Library management and safe workflows: verify asset ingestion, metadata retention, batch retimes, and rollback options; ensure safe changes that can be reversed.
Conseils de décision : concentrez-vous sur les expériences et les améliorations ; recherchez un outil qui signale une combinaison convaincante d’automatisation, d’expériences fluides et de gains à travers les productions. Une fois que vous avez exploré des essais dans des scènes variées, vous êtes en mesure de jauger la magie.
Quelles sont les réglages d'exportation qui conservent les détails photoréalistes pendant le redimensionnement et le débruitage ?
Exportation à 10 bit profondeur de couleurs Rec.709, 4:4:4 chroma, HEVC Principal 10, avec 2-pass un encodage et un débit binaire cible de 25–40 Mbps pour des livrables 4K. Les décisions concernant ce pipeline sont long et fastidieux, mais required afin de préserver les détails photoréalistes pendant le redimensionnement et le débruitage. Conserver la résolution à 3840×2160, fréquence d'images originale, et GOP around 120–180 frames. Évitez un débruitage agressif lors du passage final ; débruitez au préalable avec des bibliothèques fiables, puis appliquez un affinage léger après l'upscaling. Pour les améliorations de 1080p à 4K, appliquez gen-4-remontage ascendant basé avant l'encodage ; préserver le grain du film via les options de conservation du grain si disponibles. Si des contraintes de bande passante existent, réduire la résolution à 1920×1080 et cible 15–25 Mbps tout en maintenant une profondeur de 10 bits et une chrominance 4:4:4 aussi longtemps que possible.
Sachant que les décisions concernant le format, la qualité et la livraison prennent du temps, mettez en œuvre des pipelines reproductibles. Ce chemin est requis lorsque les équipes opèrent avec des ressources distribuées et de multiples bibliothèques à travers les régions. Un innovant approach pairs denoising first with gen-4 upscaling, puis encodage en utilisant 2-pass settings. La charge de calcul augmente ; planifiez les étapes sur les GPU dans une file d’attente continue, vous pouvez ainsi exécuter en parallèle. Si vous connaissez des modèles et des bibliothèques de confiance, vous pouvez vous y fier. recommandations de la part de réalisateurs et créateurs associés, tout en préservant l'intention artistique.
La sélection des préréglages doit s'aligner sur les plateformes cibles ; de plus, la découvrabilité s'améliore lorsque les détails à haute fréquence survivent sur différents appareils. Les réalisateurs et les monteurs en herbe s'appuient sur... recommandations de sources fiables, avec sélection données stockées dans des bibliothèques distribuées. L'examen par un humain reste required afin de valider les résultats et préserver l'intention artistique.
La création de vérifications permet de maintenir la cohérence des résultats. Surveillez les artefacts après l'upscaling ; évitez la sur-netteté ; maintenez un débruitage léger ; préservez les détails des bords ; assurez-vous que l'étalonnage des couleurs est verrouillé avant l'exportation ; maintenez les calibrations sur tous les appareils. Pour gen-4 upscaling, test sur un extrait représentatif ; conserver un petit ensemble pour comparer avant et après ; partager les résultats avec les parties prenantes afin d'affiner la direction.
Comment préparer, étiqueter et anonymiser les séquences vidéo pour un ajustement fin de modèle personnalisé
Commencez par un inventaire simple dans une base de données, associant chaque clip au projet, à la scène, au statut de consentement et aux notes de confidentialité. Ajoutez des tags décrivant le contenu, la langue et le contexte. Maintenez un vaste catalogue qui permet une recherche et une réutilisation rapides pour les tâches de réglage fin.
Définir les étapes d'anonymisation à l'avance : modifier les identités, flouter les visages, masquer les plaques d'immatriculation, supprimer les métadonnées biométriques et supprimer les coordonnées de localisation des données intégrées. Utiliser des méthodes non destructives afin que les étiquettes générées restent alignées avec la source. Tenir un registre des modifications et examiner les résultats.
Développer un schéma d'étiquetage avec une correspondance claire aux entrées des modèles en aval. Créer un document de référence avec les définitions des balises, des exemples de trames et des cas limites. Dans la mesure du possible, s'appuyer sur une couche abstraite simple pour maintenir un comportement cohérent dans différentes scènes. Utiliser hailuo comme ensemble de données de référence pour les comparaisons de référence, si cela s'avère approprié, et documenter les forces de chaque ensemble de balises pour une plus large applicabilité, comme indiqué dans les listes de contrôle de style Nelson.
Assurer le contrôle qualité en mettant en œuvre un flux de travail de révision : échantillonnage aléatoire, vérification croisée des étiquettes par rapport au contexte original, et enregistrement des mesures d'accord inter-codeurs. Maintenir les étiquettes générées alignées avec les ID de fichier et les numéros de version ; utiliser les journaux de modifications pour faciliter le retour en arrière en cas d'erreurs. Cela permet de gérer les attentes et d'améliorer la qualité des données au fil du temps.
L'automatisation de certaines parties des opérations accélère la préparation du réglage fin. Créez des pipelines légers qui copient les séquences brutes vers une zone de transit, appliquent des blocs d'anonymisation, exportent les clips anonymisés et joignent automatiquement les métadonnées ; utilisez une base de données centrale pour stocker les balises, les notes d'audit et les points de référence. Chaque fois que possible, gardez les processus simples et vérifiables. Cela améliore l'efficacité et la cohérence du processus.
La gouvernance est essentielle : définissez les contrôles d'accès, les délais de conservation et les politiques de suppression pour rester conforme aux normes de confidentialité. Élaborez un plan pour examiner les ensembles de données avant leur réutilisation et pour éviter de divulguer des éléments sensibles dans les tâches en aval. Surveillez les lacunes en matière de performance et ajustez les directives d'étiquetage afin d'élargir leur applicabilité et de réduire les biais dans les résultats générés.
Pour une amélioration continue, maintenez une référence dynamique qui capture les points forts des choix d'étiquetage et les domaines à améliorer. Explorez régulièrement de nouvelles stratégies d'annotation, documentez quelles approches fonctionnent le mieux pour les scénarios haut de gamme, et adaptez le flux de travail à mesure que les besoins s'étendent.
Comment ajouter une interpolation d'images et une synthèse de textures basées sur l'IA dans les flux de travail temporels
Commencez par activer un passage d'interpolation généré par l'IA au sein d'un système dédié, puis exécutez la synthèse de texture comme une étape distincte qui se répercute dans le contexte de la timeline. Cette approche permet de conserver un mouvement naturel et d'élargir la latitude créative sur certaines prises, offrant une base pour une exploration adaptative.
- Planifier les entrées de base : définir la fréquence d'images cible, adapter l'obturateur et réserver une couche distincte pour les images générées et les textures ; sélectionner un modèle d'interpolation basé sur l'IA (aigc) et fournir un tableau de modes aux éditeurs pour la personnalisation.
- Établir des mesures de sécurité et des protections contre les injections : exécution dans un bac à sable, validation stricte des textures générées et journalisation pour retracer les actions tout au long du pipeline.
- Fournir des commandes intuitives pour les éditeurs : curseur de fluidité des mouvements, prévisualisation, détails de la texture, seuils de clipping et une commande de mixage structurée pour aligner le contenu généré sur le rythme du plan original.
- Construisez un flux en couches : analyse d'entrée, passe d'interpolation d'images, passe de synthèse de textures, passe de composition et exportation ; l'exploration dans différentes conditions d'éclairage permet d'identifier ce qui distingue un aspect naturel cohérent.
- Options de génération d'offres : combiner les méthodes traditionnelles avec les chemins de génération génératifs ; permettre la personnalisation des palettes de textures, de la gestion des bords et de la cohérence du mouvement ; fournir un certain nombre de préréglages pour accélérer le flux de travail.
- Impliquer les parties prenantes en présentant des aperçus en direct lorsque les curseurs de la chronologie sont mis à jour ; cela encourage une exploration itérative et une prise de décision plus rapide tout au long de la production.
- Évaluer l'impact économique : un rythme plus régulier réduit les reshoots et le re-montage, permettant une livraison de produit plus efficace et des marges améliorées sur l'ensemble des projets.
- Identifier les risques : formation d’artefacts, répétition de textures ou défauts d’alignement entre les plans ; proposer des garde-fous tels que des vérifications de fidélité, une cohérence inter-plans et un retour automatique aux images sources en cas d’échec de génération.
- Sécurité et gouvernance : appliquer des flux de travail non destructifs, des contrôles d'accès pour les éditeurs et une gestion de version robuste pour permettre un retour en arrière en cas de problèmes liés à l'injection.
- Livraison et révision : livrables structurés, avec des profils d'exportation dédiés pour la qualité du produit final et une série d'aperçus pour une approbation rapide.
Cette approche distingue un domaine qui combine le contenu généré par l'IA avec l'artisanat traditionnel, permettant aux éditeurs de personnaliser les résultats tout en maintenant les contrôles des risques et la discipline budgétaire, offrant ainsi des expériences plus engageantes. Cette approche ne limite pas l'expérimentation ; elle guide des résultats cohérents et prend en charge des flux de travail sécurisés et soucieux des coûts.

 Montage vidéo en ligne – L'essor des outils de montage vidéo basés sur l'IA" >
Montage vidéo en ligne – L'essor des outils de montage vidéo basés sur l'IA" >