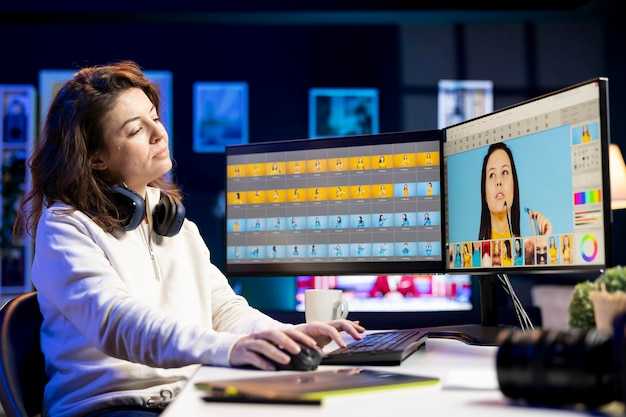
Start with an editor that automates chroma-keying, delivering colored edges and believable composites in minutes.
In an image-to-video workflow, color corrections, masks, and scene replacement are orchestrated within a single version, reducing organization overhead and enabling a lean, repeatable process. This setup is particularly valuable when you need to produce multiple takes with consistent look and bleed control.
At the Vordergrund of this space, the system supports Avatar previews and chroma-based composites, letting you scrub the scene with a user-friendly interface that mitigates a steep learning curve. They can review how colored mattes spill, checking bleed and edge quality while keeping the organization tidy and versioned.
To ensure color bleed is controlled, the editor exposes adjustable marks for chroma spill, colored fringes, and edge bleed, helping you achieve a more believable look with minimal touch-ups. The version system keeps assets organized and makes it easy to roll back if a scene changes, ensuring looks stay consistent.
As you assemble clips, the workflow remains at the Vordergrund of creation, facilitating collaboration across teams. It supports multiple asset formats, enabling you to reuse builds and publish variations quickly, including Avatar-based composites that keep the project moving even when the source material is scarce. This image-to-video approach provides enough flexibility to test ideas quickly, while accelerating delivery cycles and content testing across channels.
Main Section 2: Leveraging AI for Advanced Visual Effects Beyond Green Screen
Adopt a three-phase, fusion-based pipeline that uses a remover to isolate subjects, then a content fusion with varied backdrops, followed by a refinement feature that preserves fabric detail and neon lighting cues.
Maintain a cardboard testbed to calibrate indicators across conditions.
Phase comparisons reveal the correct balance between fidelity and expenses, opening avenues of content creation that remain affordable without compromising quality.
Guidance from technological indicators informs the approach, suggesting when to switch as conditions shift.
Apply removing edge artifacts using a remover, while a blur pass reduces edge contrast; fusion then integrates subject regions with backdrops.
The forefront of the method transforming traditional workflows into a streamlined, cost-efficient offering that can be scaled without heavy expenses.
A neon-tinted look can be achieved via a layered feature stack: base fusion, auxiliary textures, and a fine-grain refinement to color, while preserving fabric coherence.
Compare outcomes against a baseline with a formal comparison metric, using associated statistics like SSIM and perceptual scores to drive decisions.
Avenues to automation enable playing with masks across subjects and backgrounds, then streamline output under various conditions.
Phase planning yields faster cycles; ensure each phase produces correct results, with guidance on the next phase.
In summary, the described approach transforming the forefront of post-production by combining remover-driven isolation, fusion-based composition, and refinement-driven polishing.
Rotoscoping Automation: AI-assisted Edge Detection for Tight Masks
Empfehlung: Implement a two-path edge-detection workflow that starts with a fast gradient-based border detector to generate a base mask, followed by an AI-assisted refiner that tightens contours frame-by-frame, yielding clean, fill-ready edges while preserving motion continuity.
Edge detection uses gradient magnitude from Sobel/Scharr, augmented by motion cues from optical flow, with a silicon-accelerated model refining borders. This enables a tight base mask, while leaving room to adjust edges manually if necessary. The toolkit supports quick toggles to switch between conservative and aggressive masking, with clear indicators of edge strength and fill integrity. The approach is movie-grade in quality and scales to a growing range of scenes, ensuring consistency across shots.
Data and collaboration rely on supabase as the central store for masks, notes, and version history; team members log issues, attach visual previews, and link changes to campaigns; a maker-friendly toolkit yields lightworks-compatible outputs, allowing editors to pick the best path and move on to the next scene; management can monitor progress and allocate resources.
Quality control targets edge drift, feathering, and occlusions; apply color-space constraints to maintain fill consistency; implement temporal smoothing to reduce flicker and deliver a stable result; store источник metadata to trace root causes and speed corrections by the team and management.
Performance metrics measure value via edge accuracy, temporal stability, and fill quality across a growing range of scenes; dashboards reveal alignment error, latency, and throughput; teams can adjust selection thresholds to balance speed and precision, with feedback looping into the maker and creative workflow.
Practical steps include a default option pairing gradient border detection with AI-assisted refinement; tune thresholds by scene style; connect supabase to the data layer for integrity; run tests on a representative sample; collect feedback from members; refine the edge-detection models; include a green-light review step to validate edits before finalizing.
Illumination-aware Keying: Creating Natural Matte Without Green Screen

Empfehlung: Calibrate lighting in the studio with two primary sources at 45 degrees and a backlight, plus diffusion to suppress hotspots. Keep white balance neutral and constant exposure across frames. Zielen Sie auf einen dynamischen Bereich von 1,8–2,2 Blendenstufen zwischen Lichtern und Schatten ab. Dies stabilisiert das Alpha und ermöglicht eine beleuchtungsbewusste Freistellung, um eine natürliche Matte ohne Chroma-Hinweise zu erzeugen. Laden Sie einen Testsatz von 50–100 hoch. Bilder führt die Validierung im Projektarbeitsbereich schneller durch; reports das Ergebnis über viele Aufnahmen hinweg bestätigen.
Technisch gesehen, die Beleuchtungsberücksichtigende Maskierung, vermischt eine Luminanzkarte mit einer kantenberücksichtigenden Verfeinerung. Erstellen Sie die Basismatte aus einer Graustufenreferenz; wenden Sie dann einen Farbkonsistenzdurchgang an, um ungewollte Farbübertragungen zu minimieren. Bilder. Verwenden Sie ein doppelt-Pass-Ansatz, um die Kanten an jeder zu straffen Rahmen; dies bewahrt Details in Haaren, Stoffen und Texturen und erzeugt eine natürliche Silhouette, die über die gesamte Sequenz erhalten bleibt.
Arbeitsabläufe In führenden Studios setzt man auf disziplinierte Pipelines: einen stabilen link zwischen Aufnahme und Bearbeitung, verfolgen Verarbeitung Zeit und ein sauberes Erscheinungsbild zu wahren. layout im Projekt. In Premiere, lege eine zweite Matte-Ebene fest, um Restbestände zu korrigieren; vergleiche die Ergebnisse mit reports gestaffelt nach Stabilität, und dann iterieren. Dieser Ansatz setzt Anreize für effizientes Hochladen und Verarbeiten, wodurch die gesamte Studiozeit verkürzt und gleichzeitig die Detailtreue des Levels erhalten bleibt.
Praktische Schritte: Bühnenbeleuchtung im Studio, um extreme Kontraste zu vermeiden; eine Stichprobe von vielen erfassen. frames; eine Basismatte mit einer beleuchtungsabhängigen Methode generieren; mit kantenerhaltenden Werkzeugen verfeinern; validieren über presentations und minimale Vorschauen; projizieren Sie das projizierte Ergebnis zur Ausgabe in endgültigen Formaten; protokollieren Sie ein link zum Projekt und Update Bilder in Referenzlayouts verwendet. Wenn die Verarbeitung rechenintensiv ist, wechseln Sie während der Tests zu einer niedrigeren Auflösung und projizieren Sie sie dann beim Export in die volle Auflösung zurück. Dies führt zu einer effizienten workflows worauf viele Studios während Festivals und andere Zusammenkünfte.
Motion Tracking für dynamische Composites: Elemente über Aufnahmen hinweg ausrichten
Beginnen Sie mit einer präzisen Punktverfolgung bei der ersten Aufnahme und brennen Sie dann die Ausrichtung mithilfe von Keyframes in die Zeitleiste ein, um eine professionell aussehende Fusion über die Aufnahmen hinweg zu gewährleisten.
Definiere eine Mehrpunkt-Verfolgung: Wähle klar definierte Merkmale auf Oberflächen aus, die sichtbar bleiben, wie z. B. Kanten oder Texturmuster. Dieser Ansatz liefert robuste Daten, die Drifts minimieren. Verwende den Schieberegler, um Skalierung, Drehung und Perspektive anzupassen und sicherzustellen, dass die auf der Überlagerung platzierten Elemente scharf bleiben. Sorge für Lebendigkeit, indem du die Farbtreue der platzierten Überlagerungen bewahrst.
Halte den Workflow aufrecht, indem du Bewegungsdaten in zusammengehörige Ebenen gruppierst: Talentbewegung, Requisiteninteraktion und Hintergrundparallaxe. Dieser leistungsstarke Workflow hält Talente mit einbezogen, sorgt für einen reibungsloseren Ablauf und reduziert den Bedarf für extreme Nachbearbeitung.
Eine solide Planung: Lizenzfreie Musiktitel oder ein Ambient Sound Design sollten gewählt werden, die die Bewegung ergänzen. Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Wiedergabe von Sound mit visuellen Hinweisen aus der dynamischen Bewegung übereinstimmt, um das Eintauchen zu verstärken.
Eine klare Vorgehensweise für alle Aufnahmen festlegen: einen einheitlichen Farbraum wählen, bei Bedarf stabilisieren und ein scharfes Bild beibehalten, indem man zu einfache Überschärfung vermeidet. Dann Frames in der Timeline vergleichen und bei Bedarf anpassen.
| Schritt | Aktion |
|---|---|
| 1. Vorbereitungsfotos | Stabilisieren, verfolgbare Merkmale auswählen, Koordinatensystem festlegen |
| 2. Streckenpunkte | Mehrpunkt-Tracking verwenden; sicherstellen, dass Funktionen sichtbar bleiben; bei Bedarf anpassen |
| 3. Verfeinern | Manuelle Anpassungen; Okklusionen beheben; Ankerformen definieren |
| 4. Overlay anwenden | Element auf verfolgten Daten platzieren; Skalierung, Drehung, Perspektive anpassen |
| 5. Vorschau & Feinschliff | Timeline durchspielen; Keyframes anpassen; Final Pass rendern |
Tiefenschätzung für realistische Schatten und Parallaxe
Nutzen Sie die automatisierte Tiefenschätzung, um Schatten und Parallax zu steuern, manuelle Anpassungen zu reduzieren und die Konsistenz zwischen den Aufnahmen aktiv zu verbessern.
Wählen Sie schlanke Modelle, die für die Integration in Bearbeitungsabläufe optimiert sind; eine automatisierte Feedbackschleife optimiert kontinuierlich Tiefenvorhersagen, reduziert Flimmern und Kantenartefakte, ohne die Leistung zu beeinträchtigen, und dieser Ansatz funktioniert besonders gut bei variablen Lichtverhältnissen.
Die Datenstrategie umfasst synthetische Szenen, KI-generierte Texturen und eine kuratierte Auswahl echter Clips. Diese Abdeckung verbessert die Genauigkeit in verschiedenen Lichtszenarien und hält gleichzeitig die Ressourcennutzung innerhalb des Budgets vorhersehbar.
Die Integration mit der Bearbeitungsoberfläche ist entscheidend: Tiefe, Parallaxe und Schattensteuerung in einem einzigen Bedienfeld, was eine nahtlose Bedienung und fortgeschrittene technische Anpassungen ermöglicht, die sicherstellen, dass Schatten über Schnitte hinweg natürlich aussehen.
Technische Ziele: Anstreben eines mittleren absoluten Tiefenfehlers unter 0,15–0,25 m an kalibrierten Rigs; Parallaxenfehler innerhalb von 2–3 px bei 1080p halten; automatisierte Tests verwenden, um Fortschritte zu verfolgen und Verfeinerungen zu steuern. Dieser Ansatz gewährleistet stabile Ergebnisse über Sequenzen hinweg.
Abdeckungsstrategie: ein Ressourcenpaket mit Szenen, die Glas, transluzente Materialien, fließendes Wasser und unterschiedliche Beleuchtung enthalten, um die Komplexität realer Aufnahmen abzudecken.
Budgetorientierte Studios profitieren von vortrainierten Modellen, Quantisierung und Cloud-Inferenz, um die lokale Last zu reduzieren; eine movavi-kompatible Option ermöglicht es Teams, die Pipeline in bestehende Ergebnisse zu integrieren.
Ergebnis: Tiefenabhängige Schatten und Parallaxe sorgen für überzeugende Optik, selbst bei KI-generierten Eingaben; das automatisierte System unterstützt nahtlos die Bearbeitungsabläufe und bietet Optionen zur Verfeinerung jeder Aufnahme sowie zur Rückkopplung in den nächsten Durchgang.
Farbanpassung und Angleichung der Beleuchtung zwischen Clips
Empfehlung: Normalisieren Sie den Weißabgleich für die gesamte Charge, indem Sie vor der Aufnahme eine neutrale Graureferenz im Bild platzieren und dann eine einzelne Farbzuordnung auf alle Clips anwenden. Ergebnis: Kleidungsfarben bleiben natürlich, und Farbabweichungen zwischen den Aufnahmen verschwinden mit sofortigen Vorschauen auf jedem Gerät.
Prozessübersicht: Erstellen Sie eine Datenbank mit Farbprofilen pro Szene; kalibrieren Sie die Beleuchtung mit einem Belichtungsmesser; legen Sie eine Ziel-Farbtemperatur und einen Leuchtdichte-Bereich fest; wenden Sie im Batch einen LUT-Generator an, der Farbton, Sättigung und Helligkeit über Clips hinweg angleicht; validieren Sie mit Berichten, die Delta-E-Werte zeigen; streben Sie unter 2 für Hauttöne und neutrale Bereiche an; passen Sie Kurven lokal auf Clips mit größeren Abweichungen an. Die Plattform bietet eine robuste Reihe von Steuerelementen zur Angleichung von Farben.
Praktische Tipps: Verlassen Sie sich im Freien auf einen konsistenten Weißabgleich durch eine einzige Referenz; halten Sie die Richtung des Hauptlichts konsistent; wenn Szenen Kleidung mit unterschiedlichen Farben beinhalten, verwenden Sie sekundäre Steuerelemente, um Farbstiche zu vermeiden; gleichen Sie die Belichtung so aus, dass die Mitteltöne bei etwa 60-70 % des Histogramms liegen; wenden Sie bei Clipteilen mit Abweichungen lokale Korrekturen an und halten Sie die resultierenden Schatten kontrolliert; verwenden Sie Premium-Presets, um die Stapelverarbeitung zu beschleunigen und gleichzeitig Artefakte zu begrenzen.
Kernaussagen: Wenden Sie diese Schritte auf alle Videos im Batch an. Die sofortige, batchbasierte Abstimmung reduziert Nachbearbeitungen und unterstützt schnellere Bearbeitungen; führen Sie ein inhaltsweites Protokoll in Ihrer Datenbank; der Generator kann eine Reihe von gebrauchsfertigen Looks liefern; dadurch bleibt der Preis der Postproduktion kalkulierbar; lernen Sie aus jedem Projekt und verfeinern Sie die internen Richtlinien für die Beleuchtung; wenn bestimmte Kleidungsstücke immer abweichen, passen Sie die Lichtrichtung an oder fügen Sie ein Fülllicht an diesen Stellen hinzu; die Auswirkungen umfassen weichere Übergänge zwischen den Clips und ein kohärentes Gesamtbild. Berichte zeigen auf, wo Aufmerksamkeit erforderlich ist; der Batch-Ansatz hilft bei mehreren Teilen einer Szene; der Inhalt bleibt hochwertig. "Was kommt als Nächstes" erscheint in den Berichten.
 AI-Powered Online Video Editor – Green Screen for Visual Effects" >
AI-Powered Online Video Editor – Green Screen for Visual Effects" >